前言
在开发WinForm应用程序时,经常会遇到需要在线程间操作UI的情况。直接从非UI线程更新UI控件会导致异常,因此我们需要采取适当的方法来安全地进行这些操作。本文总结了几种常见的解决方法,并对其优缺点进行了分析。
正文
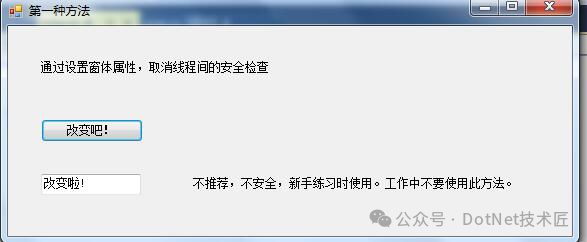
方法一:禁用线程间的非法调用检查
这是最简单的方法,但也是最不推荐的做法。通过设置窗体属性Control.CheckForIllegalCrossThreadCalls = false;可以取消线程间的安全检查,从而允许跨线程更新UI。
然而,这种方法可能导致不稳定和不安全的行为,应避免使用。
public partialclassone : Form
{
public one()
{
InitializeComponent();
Control.CheckForIllegalCrossThreadCalls = false;
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Thread listen = new Thread(new ThreadStart(receive));
listen.IsBackground = true;
listen.Start();
}
private void receive()
{
UdpClient uc = new UdpClient(5839);
while (true)
{
IPEndPoint ip = null;
byte[] message = uc.Receive(ref ip);
string messagestring = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(message);
textBox1.Text = messagestring;
}
}
}
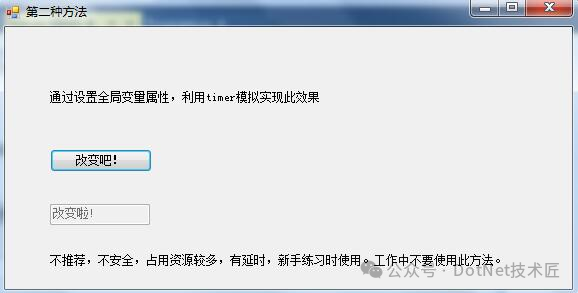
方法二:使用全局变量结合Timer实现
该方法利用了全局变量存储数据,并通过定时器(Timer)周期性地更新UI。虽然这种方法实现了目标,但由于它依赖于Timer的频率,可能会导致不必要的延迟和资源消耗。
public partialclasstwo : Form
{
string messagestring = "";
public two()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void two_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Thread listen = new Thread(new ThreadStart(receive));
listen.IsBackground = true;
listen.Start();
timer1.Start();
}
private void receive()
{
UdpClient uc = new UdpClient(5839);
while(true)
{
IPEndPoint ip = null;
byte[] message = uc.Receive(ref ip);
messagestring = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(message);
}
}
private void timer1_Tick(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
textBox1.Text = messagestring;
}
}
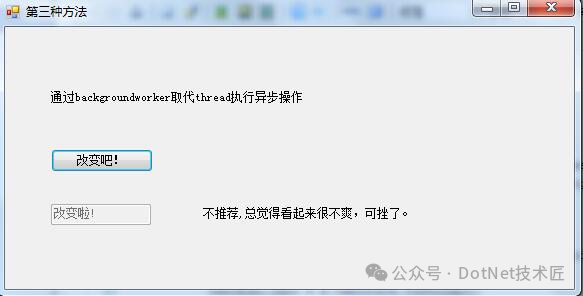
方法三:使用BackgroundWorker组件
使用BackgroundWorker可以简化异步编程模型,适合处理简单的后台任务。
但是,它的局限性在于仅适用于Windows Forms,对于其他平台则不适用。
public partialclassthree : Form
{
public three()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void backgroundWorker2_DoWork(object sender, DoWorkEventArgs e)
{
UdpClient uc = new UdpClient(5839);
while(true)
{
IPEndPoint ip = null;
byte[] message = uc.Receive(ref ip);
string messagestring = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(message);
backgroundWorker2.ReportProgress(50, messagestring);
}
}
private void backgroundWorker2_ProgressChanged(object sender, ProgressChangedEventArgs e)
{
textBox1.Text = e.UserState.ToString();
}
}
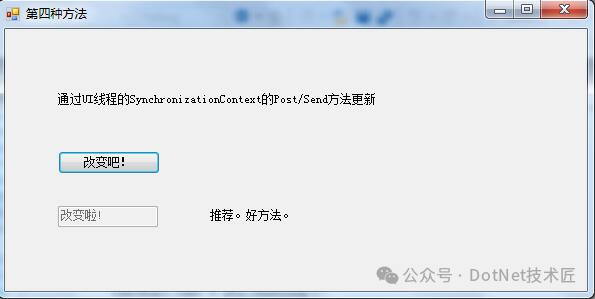
方法四:使用SynchronizationContext
通过SynchronizationContext的Post或Send方法可以在不同线程之间传递消息,确保UI更新安全执行。
这是一种较为灵活且可靠的方式。
public partialclassfourth : Form
{
SynchronizationContext SyncContext = null;
public fourth()
{
InitializeComponent();
SyncContext = SynchronizationContext.Current;
}
private void receive()
{
UdpClient uc = new UdpClient(5839);
while (true)
{
IPEndPoint ip = null;
byte[] message = uc.Receive(ref ip);
string messagestring = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(message);
SyncContext.Post(change,messagestring);
}
}
private void change(object str)
{
textBox1.Text = str.ToString();
}
}
方法五:使用Invoke或BeginInvoke
这是目前最常用的跨线程更新UI的方法。通过控件的Invoke或BeginInvoke方法将委托调度到UI线程上执行,保证了线程安全性。
public partialclassfifth : Form
{
delegate void Change(string text);
public fifth()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Settext(string text)
{
textBox1.Text = text;
}
private void receive()
{
UdpClient uc = new UdpClient(5839);
while (true)
{
IPEndPoint ip = null;
byte[] message = uc.Receive(ref ip);
string messagestring = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(message);
this.BeginInvoke(new Change(Settext),messagestring);
}
}
}
总结
跨线程操作UI是WinForm开发中常见的挑战之一。尽管有多种方式可以解决这个问题,但考虑到安全性和灵活性,推荐使用SynchronizationContext或者控件的Invoke/BeginInvoke方法。正确理解并应用委托机制对有效管理多线程环境下的UI更新至关重要。
关键词
#WinForm、#跨线程操作、#UI更新、SynchronizationContext、#Invoke、#BeginInvoke、BackgroundWorker、Timer、#线程安全
阅读原文:原文链接
该文章在 2025/7/2 0:28:54 编辑过